RPA Genie Administrative Console
The RPA Genie Administrative Console is a diagnostic tool that can assess functionality, guide users about the status of a particular functionality, and let users review and modify the settings that regulate the way RPA Genie Service operates. It will be installed at the same time as the RPA Genie service and will be available on the Genie Server.
Welcome Page
In the “Home Page” of the RPA Genie Admin Console, we can view the Service diagnostic Summary and Health monitoring status.

In the “Service Diagnostic Summary” section, the following fields can be seen:
- Website Name: In this field you can see the Website name of the RPA Genie Service.
- Service URL: This field displays the Service URL of the RPA Genie Service.
- Application Pool: The field shows the Application Pool name of the RPA Genie Service.
- Machine Name: This field will display the user Machine name where the RPA Genie Service is deployed.
- Version: The currently installed version of the RPA Genie Service will be shown in the Version field.
The “Health Monitoring” section includes the following fields:
- Application Pool Status: The Application Pool Status for the RPA Genie Service will indicate whether the Application pool has Started or Stopped.
- Genie Database Status: The status of the connection between RPA Genie Service and the Genie Database (i.e., Connected or Disconnected) can be checked by the user through this field.
Diagnostic Page
The user will be redirected to the Genie Diagnostic Validation when they click on the “Diagnostic” section of the RPA Genie Admin Console, where six primary validations are listed, as follows:
- RPA Genie SQL Connectivity Validation
- AppForms SQL Connectivity Validation
- RPA Genie URL validation
- RPA Genie Application Pool Validation
- RPA Genie Server Certificate Validation
- DotNet Version Validation

The ![]() (tick mark) next to each validation indicates that there have been no validation errors. But if any of the validations has a
(tick mark) next to each validation indicates that there have been no validation errors. But if any of the validations has a ![]() (cross mark) next to it, then the user can check the error by simply clicking on that particular
(cross mark) next to it, then the user can check the error by simply clicking on that particular ![]() (question mark) icon. Next, a wizard will appear and suggest possible resolutions as illustrated below:
(question mark) icon. Next, a wizard will appear and suggest possible resolutions as illustrated below:

As shown in the above figure, an error has occurred when RPA Genie SQL Connectivity was being validated. On clicking the ![]() (question mark) icon, a pop-up wizard will be displayed with a list of all possible solutions.
(question mark) icon, a pop-up wizard will be displayed with a list of all possible solutions.
The following list of potential fixes has been provided for each validation if any of the validation is unsuccessful:
RPA Genie SQL Connectivity Validation
- Check if the SQL Server is Operational.
- Check if the SQL Service is Running.
- Check if the network connection is stable.
AppForms SQL Connectivity Validation
- Check if the SQL Server is Operational.
- Check if the SQL Service is Running.
- Check if the network connection is stable.
RPA Genie URL validation
- Check if the RPA Genie Service site is running.
RPA Genie Application Pool Validation
- Check if the RPA Genie Application Pool is running.
- Check and validate the RPA Genie Application Pool User Credentials.
RPA Genie Server Certificate Validation
- Check if the Certificate bound with the Genie Service is Valid.
- Check if the Certificate is Expired.
DotNet Version Validator
- Check if the dot net core version is updated or not.
Settings Page
We can access a list of options in the RPA Genie Admin Console by clicking on the “Settings” tab, as illustrated in the image below.

IIS

IIS, or Internet Information Services, is a web server software by Microsoft that is used for Windows servers. It is utilized to host and manage websites, web applications, and services.
From the IIS page of RPA Genie Admin Console, users can configure the following fields:
- Service Website Name: The website name of the RPA Genie Service will be displayed in this field.
- Website Location: The location of the RPA Genie service that is installed on your machine will be displayed in the Website Location field.
- Host Name & Port: The hostname and port number of the RPA Genie Service can be visible in this field.
- SSL Certificate Subject or Thumbprint: In the SSL Certificate dropdown list, the user can see all the available certificates in the user Domain and also can bind any of the certificates with the IIS Settings of RPA Genie Service.
AppForms Database

Authentication methods are stored and managed centrally in the AppForms DataBase. It enables us to securely store and access authentication information, such as usernames and passwords, which can be used to confirm the legitimacy of users accessing applications or systems while improving security and access control.
The RPA Genie Admin Console’s AppForms Database page allows the user to make changes to the following fields:
- SQL Server Host: This shows the AppForms Database SQL Server Host of the RPA Genie Service.
- Database Name: The AppForms Database Name of the RPA Genie Service is shown in this field.
- Authentication: The user can test the AppForms’ database connection as well as the connections for Integrated Windows Authentication and SQL Server Authentication in the authentication field.
- Username: The username of the user connected to the AppForms Database is displayed in the Username field.
- Password: The user’s password connected to the AppForms Database is displayed in a masked format in this field.
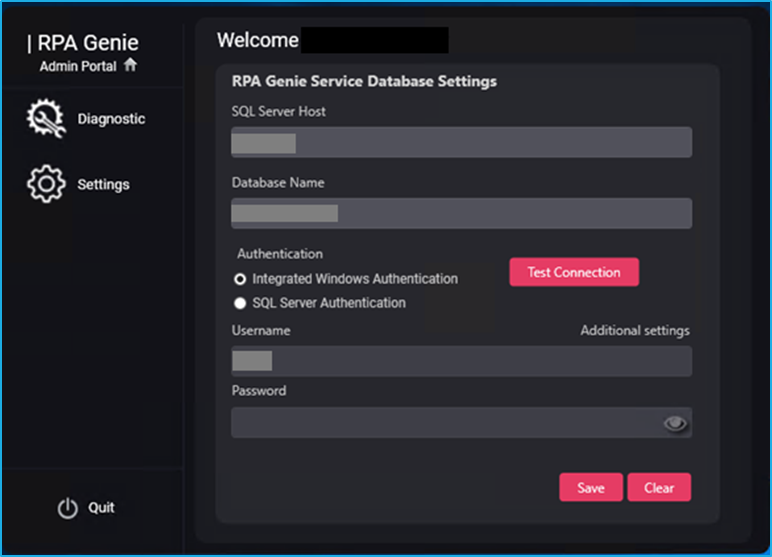
Genie Database
Additional Settings Wizard:

The Genie Database acts as a comprehensive storage system for storing all metadata associated with a particular application or system. For effective data management, retrieval, and manipulation for various processes and functionalities, it preserves key information about data structures, configurations, and relationships within the application.
The following fields of the Genie Database page are editable by the users:
- SQL Server Host: The Genie Database SQL Server Host of the RPA Genie Service will be shown in the SQL Server Host field.
- Database Name: The Genie Database Name of the RPA Genie Service will be shown in the Database Name field.
- Authentication: In the Authentication field, the user will be able to test the Database Connection of the Genie and can test the connection of Integrated Windows Authentication and SQL Server Authentication.
- Additional Settings: By clicking on the additional settings, the user will be able to add additional properties to the connection string in the form of a Key value pair.
- Username: The Username of the user connected to the Genie Database can be seen in the Username field.
- Password: The user’s password connected to the Genie Database will be shown in a masked format in this field.
Application Pool
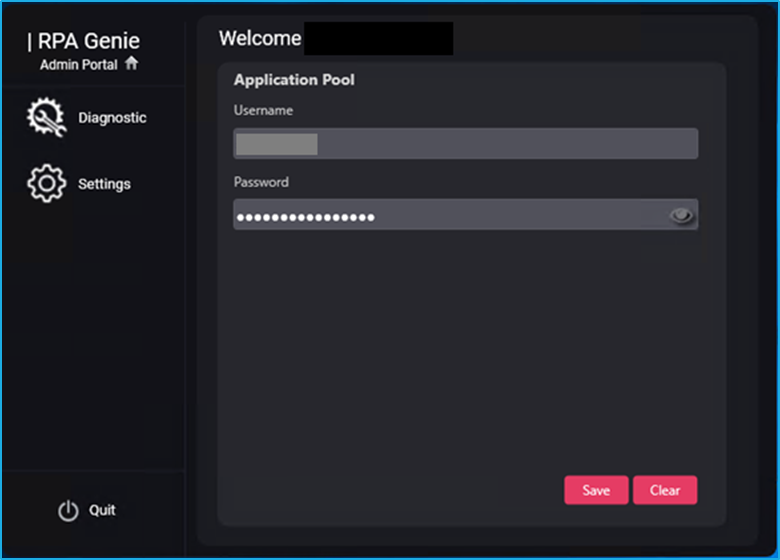
An application pool is a feature of the web server software (like IIS on Windows) that isolates and maintains web applications by giving them their own process space and resource allocation. Through the Application Pool page users can configure the username and password.
- Username: The Username of the application pool identity of the RPA Genie Service Application Pool will be shown in this field.
- Password: The Password of the application pool identity of the RPA Genie Service Application Pool will be shown in a masked format in the Password field.
Mail Notification

The Mail Notification page provides users with the ability to customize email-related settings. These settings help users to tailor their email notifications according to their preferences and needs.
- Mail Polling Interval (Min): Mail Polling Interval refers to the frequency specified in minutes at which an email must be sent to the client if an issue occurs in the service configuration or app settings of the RPA Genie Service.
- Notification Engine: Users have the option to choose their mail notification engine, which can either be Microsoft or MailKit, from a dropdown menu for accessing their emails.
If the “Use Default” checkbox is checked, then the default credentials will be used to send the
mail through the Microsoft server. If it is unchecked, then the mail is sent with the respective SMTP credentials provided in Bot Manager. This is only applicable to Microsoft SMTP Server.
Robot Connection
A robot connection configuration defines the connection frequency, ping intervals, and idle timeout parameters used by a robot to communicate with a Service URL. Additionally, it controls how robots interact with the Service URL, determining whether they can connect automatically or whether they must manually register.

The Robot Connection page enables the user to customize the following fields:
- Interval (Min): This field specifies the number of times (in minutes) that a robot connects to the Service URL.
- Ping Time Interval (Min): The frequency or time interval (in minutes) at which a service notifies the user whether or not a robot is still connected to the service URL.
- Disconnected Idle Timeout (Min): The time limit up to which the Bot tries to re-establish the connection with the RPA Genie Service. After the specified time limit the status of the Bot will change to disconnected.
- Connector: Connection with the robots to the Service URL will be established only if the “Enabled” checkbox is checked. Using this feature, we can restrict the robots from getting connected to the Service URL. Whenever the user opens the Copilot or the Agent it will automatically enroll or sign up, if the “Auto Register” feature is enabled without performing manual registration or input of personal information.
Machine Connection
Machine connection refers to the process of establishing and managing the network connection between a machine and a designated Service URL. Users can configure settings like connection frequency, disconnection idle timeout, and unique identifiers from the Machine Connection page to enable communication and data exchange between the machine and the designated service.
- Interval (Min): The frequency or time interval (in minutes) at which a machine establishes a connection with the Service URL.
- Disconnected Idle Timeout (Min): The interval (in minutes) after which the machine’s state will be marked as disconnected once the machine gets disconnected from the Genie Service.
- Device Id
- Machine ID: A machine ID is a unique code or a number assigned to a computer or device, serving as a unique identifier for the system.
- Machine UserId: This field creates an individual identifier for a particular computer or device by combining the machine name and username, which are separated by a hyphen.
Job Scheduler
A job scheduler automates job execution by defining how often specific jobs will be running, their active execution intervals, and the maximum idle time before termination.

Following are the fields that the user can edit from the Job Scheduler page:
- Schedule Job Interval (Min): The time duration or frequency (in minutes) can be configured in this field to run a specific job or task automatically in a scheduled manner.
- Running Job Interval (Min): The Running Job Interval specifies the time interval or frequency (in minutes) at which a job or process is actively running or executing.
- Disconnected Idle Timeout (Min): In this field, we can specify the maximum period of inactivity allowed for a job to remain disconnected (not actively processing) before it is terminated or marked as inactive by the scheduler.
Shared Location

- Shared Location: This field indicates the same shared place from which the installation bundle, packages, and extensions can be accessed. Also, the user will be able to change the shared location path and configure it to a different location, so that all the files will be accessible from that configured location.