In this digital era, increased businesses and industries are automating their workflows and operations. As for some industries who think automation is a costly effort, they are witnessing early adopters of robotic process automation outperform the rest of the organizations with an increased ROI and also round-the-clock work at reduced costs.
According to a recent Forrester Report, RPA will be worth $2.9 billion by 2021. RPA is a technological breakthrough for industries as they automate the entire business workflows efficiently.
Top Use Cases Of RPA Implementation
- Telecommunications
- Banking
- Customer Care
- Insurance
- Healthcare
- Manufacturing
- Finance
- Property Management
- Retail
- Information Technology
Robotic Process Automation allows industries to automate tasks across various systems. An industry that implements RPA can automate its entire workflow, infrastructure, and other backend processes, which are mostly labor-intensive and time-consuming.
Industries of all sizes can automate their tasks with robotic process automation that completely eliminates the risks of human errors. Let us walk through the key use cases of RPA implementation in various industry verticals:
RPA In Telecommunications
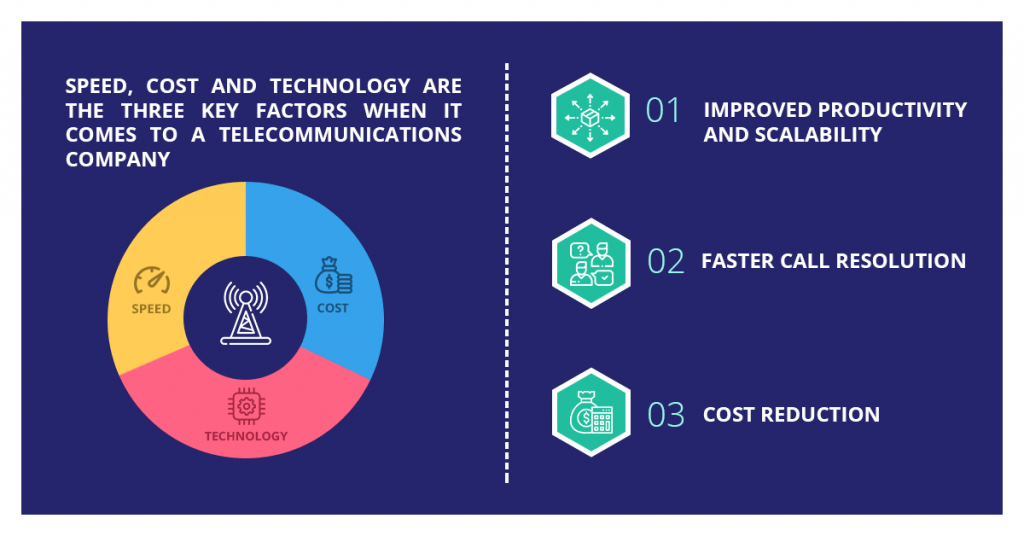
Speed, cost and technology are the three key factors when it comes to a telecommunications company. Telecom companies can take advantage of RPA in the following key areas:
Improved Productivity and Scalability
The ability to handle large volumes of data makes the robotic process automation the best suitable go-to-market strategy for the telecommunications industry. Being able to automate back-office processes eliminates the need for employees to perform redundant tasks and focus on other critical tasks.
First Call Resolution Benefits
RPA enables software bots to rapidly access data, thus helping the telecom agents address the customer demands on their first call without having to perform repeated follow-ups. RPA promotes FCR rates thus ensuring customer retention and loyalty.
Cost Reduction
The major cost reduction involved with implementing RPA in telecom is that the RPA software license can be used for multiple processes. The implementation cost is also not as high as that for ERP or Business Process management. Automating tasks also leads to increased ROI.
RPA In Banking
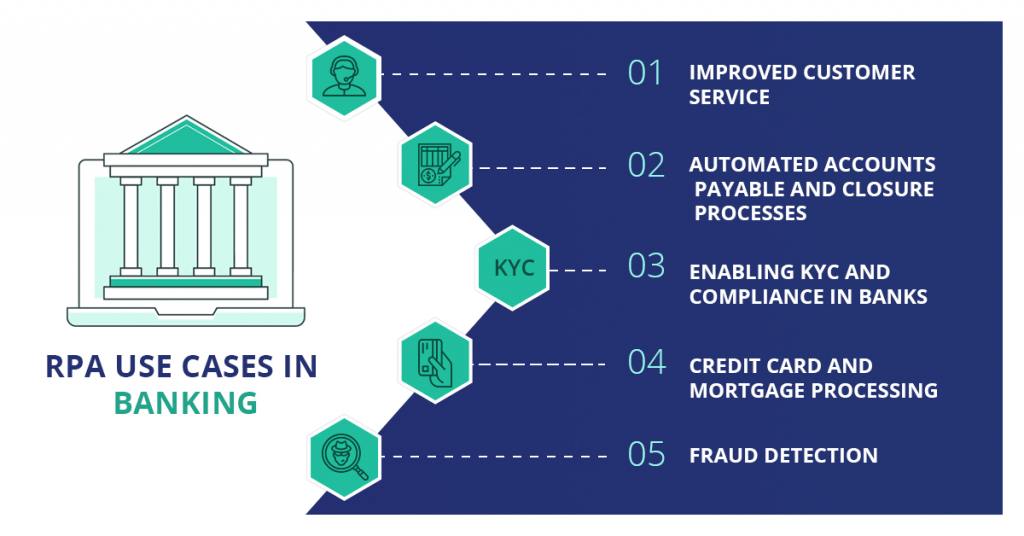
Incorporating RPA saves labor and operational costs in banks. It also reduces errors and human tasks significantly. For instance, the processing cost reduces to 30% to 70% by reducing the turnaround time with banking automation via RPA technology. The banking sector can leverage RPA in the following ways:
Improved Customer Service
From customer on-boarding, verifying customer details to account and loan inquiry, RPA helps banks reduces the turnaround time. This helps banks retain their customers and maintain customer loyalty.
Automated Accounts Payable and Closure Processes
The Traditional process of AP involves gathering invoices from vendors using OCR (Optical Character Recognition), validating the data in the fields thus provided and then processing it. RPA automates this entire process and credits the amount automatically to the vendor’s account.
RPA also sends automated notifications to customers prompting them to furnish necessary documents and processes account closure functions with 100% accuracy.
Enabling KYC And Compliance In Banks
Statistics show that certain banks invest in KYC compliance figures that are close to $384 million every year. RPA is used to gather customer information, validate and process it. Fewer FTEs and round-the-clock functioning improve productivity and the quality of the compliance process.
Credit Card And Mortgage Processing
RPA speeds up the credit card dispatching process by automated background checks and validation based on given rules and procedures. As with mortgage processing, banks have to perform several scrutiny checks such as employment and credit history, etc. RPA implementation speeds the entire process based on well-defined algorithms.
Fraud Detection
Potential frauds are identified before-hand with the advent of RPA. Automating has led to banks being able to identify accounts that are likely to cause threats and flags them. Banks can thus scrutinize these accounts and initiate fraud investigation.
RPA For Customer Care
Amongst the industries embracing RPA benefits, the customer care industry is no exception. When it comes to rule-based redundant work, robotic process automation can be relied upon by BPOs. The different RPA use cases in customer care are as follows:
Automated Data Exchange
Customer care executives operate in a data-driven world. Critical data about customers is gathered and insights are drawn from it. RPA automates the entire process and helps save time and costs by serving their customers better and faster.
Cost Control
According to the Institute of Robotic Process Automation, adoption of RPA reduces operating costs by 25-50%. Operating costs are reduced with RPA implementation by allocating redundant tasks to these software bots. This also helps outsourcers and clients to improve sales.
Accurate and Differentiated Workflows
With very less human intervention, the workflows are accurate and are performed at a fast pace. Leaving repetitive tasks to be performed by the software bots, there is a minimum number of the workforce engaged in the process. This not only brings more accuracy but also avoids additional costs and saves time.
Offering differentiated and customized services to customers can be obtained by implementing RPA in industrial operations. This helps to maintain customer loyalty.
RPA In Insurance
Collecting important data and automating repetitive tasks is essential for the insurance industry. For ensuring a better customer experience, the insurance industry makes use of the following RPA use cases:
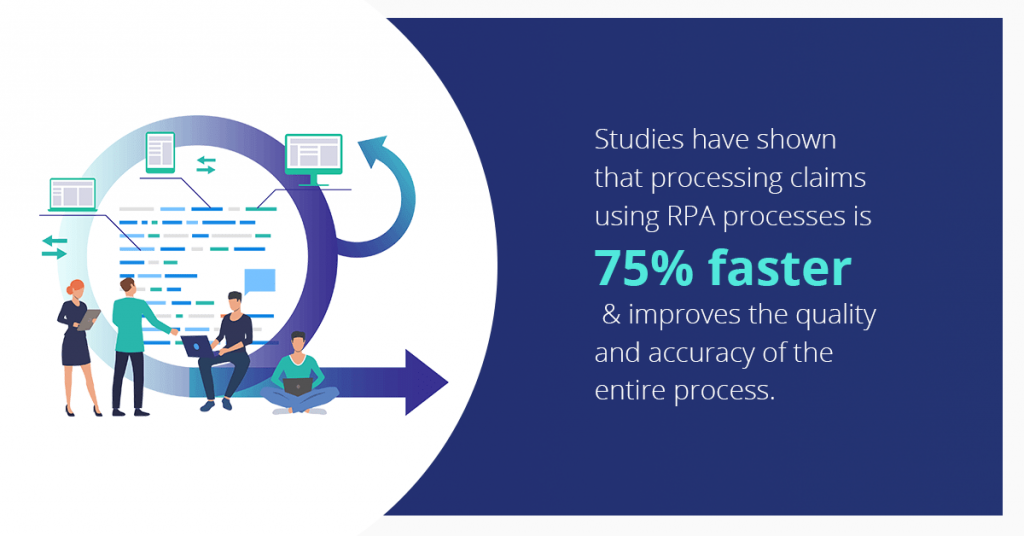
Processing Claims
Studies have shown that processing claims using RPA processes it 75% faster than the traditional approach. Paper-based processes are eliminated by RPA which improves the quality and accuracy of the entire process.
Form Registration Process
Insurance automation with RPA speeds up the form registration process by 40%. RPA with artificially intelligent systems reduces the workload significantly and ensures customer satisfaction.
Regulatory Compliance Updates Made Simpler
Insurance firms rely on several compliance standards and policies. For instance, the HIPAA privacy rules and PCI standards can vary and banks can help their clients stick to these compliance standards by making use of automated notifications and updates using RPA strategies.
Risk Mitigation
RPA allows risk mitigation via RPA by being able to accurately process data automatically from both internal as well as external sites. This ensures delivery of work at a faster pace and with 100% accuracy.
RPA In Healthcare Industries
With the growing volume of patients, healthcare industries are prioritizing on cost reduction and efficiency as two major benefits of RPA implementation in healthcare services. The key RPA use cases in healthcare are as follows:
Savings on Human Workforce
Replacing the workforce that performs mundane and repetitive tasks can be replaced with RPA implementation. This helps the workforce from spending time on core activities rather than perform intense and mundane tasks.
Increased Throughput With Improved Quality
Healthcare personnel can now tackle the large volume of patients, especially in providing individual care and attention. Maintaining medical records of patients, entry processing, claim processing, etc are automated with lower costs via RPA implementation.
RPA In Manufacturing Industries
Robotic process automation has made manufacturing companies shift their production units to automated software bots. Assembling of products, quality checking and packaging and back-end processes have obtained a 40% savings in operational costs via automation. The major use cases are as follows:
BOM Made Simple
The Bill Of Materials with the list of raw materials for new product creation provides detailed information. Leveraging RPA makes product creation faster and ensures accurate and timely creation.
Data Migration
Unlike traditional data migration, implementing RPA provides proper planning and execution of moving data from old to new systems, ensuring cost and time savings.
ERP Automation
Planning of resources is made easier with RPA implementation. Managing Inventory, Accounts Payable, Receivable, and other reports are generated automatically.
Apart from these key areas, other industries that leverage robotic process automation strategies are as follows:
RPA In Finance
Managing customer accounts, creating various reports, migrating data between accounts, updating loan and mortgage data, etc are major applications
of RPA in the finance sector. RPA helps financial services meet compliance standards with changing rules.
RPA technology is accurate and hence implementing RPA in financial services provide significant risk reduction. Faster RPA cycles enhance finance processes, is highly scalable and rapidly deployable.
RPA In Property Management
Property owners are able to manage their property units systematically with RPA. Automated processes help property owners reduce the turnaround time, improve the efficiency of business processes, and save costs.
RPA In Retail Sector
RPA provides the retail industries with solutions such as automatic inventory monitoring, email sales, extraction of critical information from manufacturer websites, etc.
RPA In Information Technology Industries
From employee onboarding, due diligence, payroll processing, task tracking to CRM updating, leveraging RPA in the Information Technology sector can benefit by automating the highly repetitive tasks. Additionally, it helps in saving costs and time.
Need a step-by-step guide on how to implement RPA to your business for positive outcomes? Call our experts right away to learn more about RPA for your industry!