What is Robotic Process Automation? RPA Explained
Automation has become a transformative element in today’s business world, changing the way businesses operate. Robotic Process Automation is at the forefront of automation that is getting popular across various industries.
While many organizations have embraced this technology, there are still others who have yet to implement it in their field due to many concerns and confusion.
What is Robotic Process Automation?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is a technology in which software bots are used to automate monotonous tasks in a digital environment. Using RPA technology, bots are deployed to seamlessly perform manual and repetitive tasks such as filling out forms, data entry, calculations, etc.
In robotic process automation, the term ‘robotic’ denotes software bots executing tasks. Here, RPA learns a sequence of events and automates the business process with the least amount of human intervention.
RPA software
RPA software refers to software tools used for automation that develop, deploy and manage Robotic Process Automation solutions. These tools provide a platform to create and configure bots for automating business processes.
UiPath, RPA Genie, and Blue Prism are some of the popular RPA software available in the field.
What are RPA bots?
Automating repetitive and mundane tasks performed by humans is the main objective of RPA bots. The RPA bots can execute certain tasks independently as well as under the supervision of employees if it is rules-based.
RPA bots can automate processes, including
- Create files and folders.
- Setting up and removing apps
- Glean data and information from optical character recognition.
- Helps transfer data between multiple systems
- Filing forms, typing messages, and more.
Types of RPA
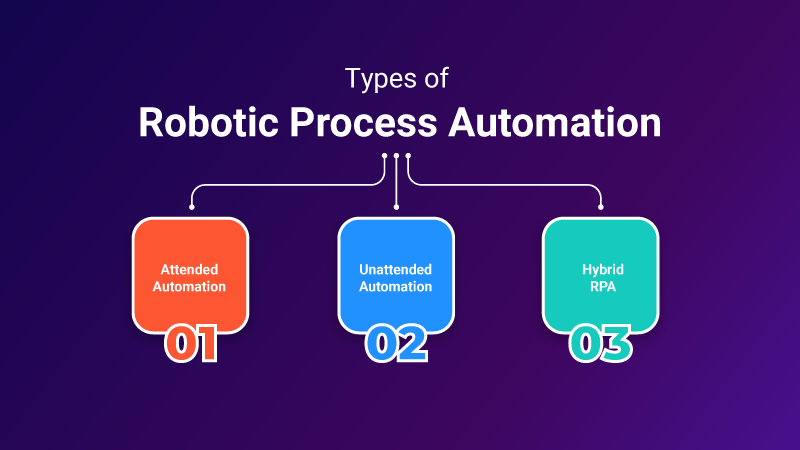
RPA can be classified into three types: attended automation, unattended automation, and hybrid RPA.
Attended Automation
Attended automation is a type of RPA that requires human intervention. This sort of automation is done when users are in front of the system. This is used to automate smaller tasks at an individual level. In this scenario, when a human triggers or initiates a process, RPA will execute the tasks. This is mainly used for front-office tasks.
Unattended Automation
Unattended automation is a type of RPA that does not require human intervention. It is automatically triggered as soon as a computer or server is set up to run the automation process for the user. In effect, unattended automation can execute long and complex processes independently. This is used for tasks such as manual data entry, record maintenance, etc.
Hybrid RPA
Hybrid RPA is a combination of both attended and unattended automation. Here, automation tools and the human workforce work together on monotonous tasks. In some scenarios, creativity and decision-making skills will have to be used along with automation tools to bring out the best outcome. In this way, hybrid automation works by providing human input to automation tools. This is used for both front-end and back-end tasks.
How does Robotic Process Automation Work?
RPA Implementation
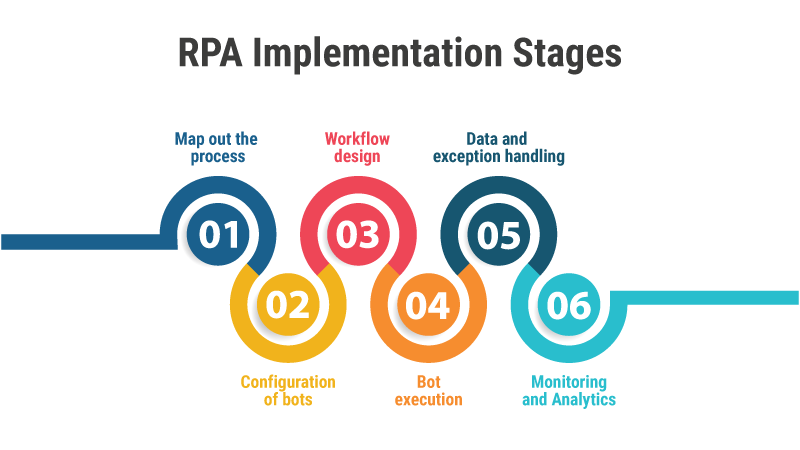
Process discovery is the initial stage in automating any task. This involves identifying and understanding the manual and repetitive tasks performed by workers in the organization. Listed below are the steps and stages of RPA implementation :
Map out the process
The tasks that fit for automation are well-defined and mapped out to learn the workflow and dependencies. This process involves locating input data, actions to be executed, etc.
Configuration of bots
RPA software helps companies to configure bots to execute specific tasks. These RPA bots are trained to navigate across various applications and perform various actions such as interacting with user interfaces and extracting input data etc.
Workflow design
RPA software’s user-friendly interface enables users to create automation workflows. These workflows are created by specifying the sequence of actions that the bots will execute. Users can select from pre-built automation components that can be dragged and dropped or they can create custom logic as per the needs.
Bot execution
After the workflow is set up, bots will execute the defined actions.
Data and exception handling
RPA bots can handle structured and semi-structured data. These bots can extract data from various sources and validate and populate it into various systems and applications. RPA software is capable of handling exceptions or errors that may happen during automation.
Monitoring and Analytics
RPA software offers robust monitoring capabilities to track the performance of bots, audit trails, and generate valuable analytics. These features help an organization recognize bottlenecks, measure the efficiency gains and improve the automation process.
Implementation of RPA can vary based on factors such as the choice of RPA software, the complexity of tasks being automated, and the needs of the organization.
RPA challenges
RPA faces many challenges during planning and implementation. Some of the RPA challenges include resource constraints, lack of infrastructure, high cost of implementation due to lack of skilled resources, etc. Some of these challenges in RPA affect small businesses more than they do for larger enterprises. Picking the right tool is part of solving this problem as it saves much cost in terms of licensing fees, resourcing, maintenance, etc.
Benefits of RPA (Robotic Process Automation)
Here are some of the key benefits of RPA:
Accuracy and efficiency
RPA reduces errors and improves task efficiency.
High productivity
RPA frees up employees for more high-value activities, increasing productivity.
Cost-effectiveness
RPA reduces operational costs and offers a quick ROI
Hassle-free automation
RPA integrates with legacy systems, requiring no changes in code.
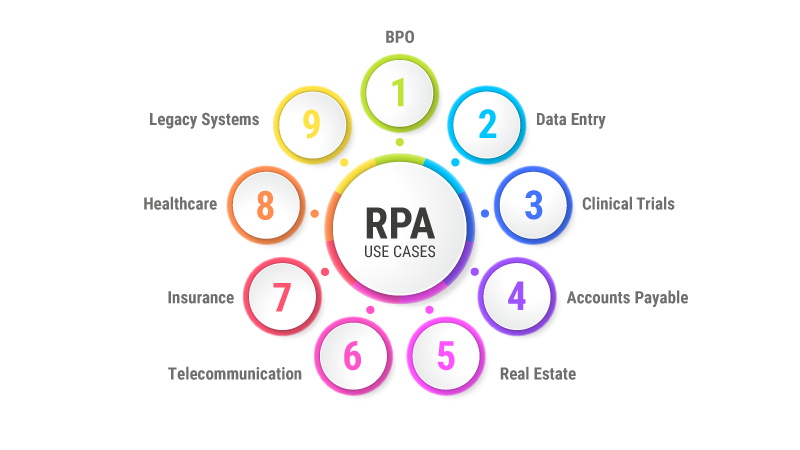
Use cases of Robotic Process Automation
Let us discuss some of the main use cases of RPA:
RPA in Data Entry
RPA bots are good at data entry tasks like extracting data from PDF formats, converting PDF into Word, filling online forms, and simplifying file conversion.
RPA in Clinical Trials
RPA software is vital in clinical trial processes, matching patient health records with criteria, monitoring progress, and scheduling follow-up appointments.
RPA in Accounts Payable
RPA streamlines account payable tasks such as invoice processing, payment verification, extracting and validating invoice data, automating purchase orders, etc.
RPA in BPO
RPA enhances customer service by collecting and giving more information about the customers’ queries and automating data entry and validation processes.
RPA in Real Estate
RPA automates tasks in real estate like data entry, documentation, property management, and lease administration.
RPA in Insurance Industry
RPA streamlines policy management, claims processing, underwriting, and data entry in the insurance industry.
RPA in Healthcare
RPA automates appointment scheduling, billing, and patient communication in healthcare.
RPA in Telecommunication Industry
RPA automates customer onboarding, billing processes, and data access in the telecom sector.
RPA Tools
How do I choose the right RPA tool?
First and foremost, we have to keep in mind the objectives and goals of the organization when adopting RPA. Though RPA tools must be chosen based on our requirements, there are some common criteria we can adopt here:
Ease of implementation
Since it is a new technology for an organization, it must be easy to implement and integrate with the existing legacy system. Then only can we reduce the downtime and make an easy transition to automation.
Ease of use
The tools must be user-friendly and flexible to get on with the basic automation process. It should require only less training to control the RPA system even for employees who lack knowledge of programming
Technical capabilities
A company has to look for technical capabilities such as scalability, screen scraping, cognitive capacities, etc. in RPA tools. As RPA bots deal with private and confidential data, standard security features must be available in the tool.
Cost
The RPA tools available on the market differ in their costs based on their features. Hence, you have to choose the tool based on your requirements and affordability. If you run a small organization, it is hard to afford and implement high-featured RPA tools.
Top Robotic Process Automation RPA Tools
RPA is an advancing field of technology, and many RPA tools are available on the market now. Let us discuss some of the popular RPA tools.
RPA Genie
RPA Genie is a popular RPA tool developed by ClaySys Technologies. It is a great platform with core capabilities of automating all types of monotonous tasks. RPA Genie has been used to automate repetitive tasks in various industries including banking, finance, credit unions etc.
Blue Prism
As an RPA tool, Blue Prism provides all core capabilities. It supports any platform and works with any application. Though you should have programming skills to use this tool, it is user-friendly for developers.
UiPath
UiPath is a popular RPA tool that helps businesses to automate their business processes. It provides well-defined features for managing automation workflow. UiPath provides flexibility in deployment models by supporting attended and unattended automation.
Automation Anywhere
As a popular RPA tool, Automation Anywhere has powerful automation capabilities that help to automate a wide range of tasks such as desktop automation, web automation, data extraction, etc. It also supports integration with external systems and applications.
How do RPA and AI relate?
What is AI?
Artificial intelligence is a technology that equips machines to simulate human intelligence and perform intelligent tasks. The application of AI has been evident across various industries and even in our daily lives. Smart gadgets, autonomous cars, and chatbots are some of the use cases of AI in our everyday life.
How do RPA and AI relate?
RPA and AI have many things in common. Both are promising technologies that help businesses and organizations with digital transformation. By combining both RPA and AI, we can implement a sophisticated form of automation called intelligent automation. Here, tasks that require human judgment and intelligence can also be automated by integrating RPA and AI technologies such as NLP, ML, etc.
Robotic Process Automation Vs. Intelligent Automation
What is intelligent process automation?
Intelligent Process Automation (IPA) is an automation technology that combines RPA and AI technologies. By bringing together RPA and AI, IPA implements a cognitive level of automation that can handle complex, unstructured, and non-routine tasks.
RPA vs. IA
Even though both RPA and IA are technologies used for automation, there are some key differences.
- RPA automates routine and rule-based tasks using software bots. It mainly handles structured and predictable tasks with a set of rules. However, IA is a more advanced technology for automation that uses RPA and subsets of AI such as NLP, ML, and intelligent document understanding. It can use cognitive capabilities so that IA can handle unstructured, complex tasks that demand human judgment and intelligence.
- Another key difference is regarding the ability to learn and adapt to new situations. RPA is designed to perform specific tasks with a predetermined set of rules. Hence, it cannot handle anything beyond what it is programmed to do. However, IA can learn and adapt to new situations, allowing them to handle complex and unpredictable tasks.
Future of RPA
The future of Robotic Process Automation is going to be all about how RPA tools integrate successfully with other technologies. For instance, the latest trend in automation is intelligent automation (IA). IA is the advanced form of automation that results from combining RPA and AI technologies. This helped the RPA bots go beyond their traditional boundaries of automating only routine and mundane tasks. Here, this integration of two technologies made it possible to add an element of intelligence, and the tasks of a more intelligent nature can be performed successfully. Predictably, an advanced form of intelligent automation will be the future of RPA.
In addition, for the time being, the potential of RPA is fully harnessed by large entities or organizations. Many small and medium-scale industries are not fully receptive to this technology for many reasons. Indeed, it will change gradually, and all sorts of industries, from small-scale to large-scale, will adopt it in their business processes.
Wrap-Up
As organizations and businesses grow and strive to achieve more, they have to work out strategies and implement them accordingly. Automation and RPA are trends in the domain of technology that have helped employees be more productive and creative. Since mundane tasks in high volume can be easily handled by RPA bots, it ensures that the tasks are error-free, and the employees are able to focus on other intelligent tasks. Of course, RPA technology is evolving, and we are expected to witness its wider and more advanced application in every sector.
FAQ
RPA is an automation technology that makes the automation of business processes more efficient, error-free, and effective. But it is also possible to fail for several reasons. RPA can fail due to unrealistic goals, choosing non-ideal processes, and its inability to learn and respond to unexpected events.
Process mining is used to monitor the execution of the processes in the organization and discover how the processes are performed. This helps us understand the inefficiencies of the processes and point out the places where improvement is required.
Hyperautomation is an advanced form of automation that automates as many business processes as possible using different technologies such as RPA, AI, and ML. It automates not just repetitive, rule-based tasks but also complex tasks that require human intelligence to perform the tasks.
RPA poses security challenges, including the need for audit logs, supervision of bots, preventing data misuse, and cyber security vulnerabilities related to different layers involved in automation. We always have to be kept on alert to protect against cyber threats.